Orifice Discharge into Free Air
An orifice is an opening with a closed perimeter through which water flows. Orifices may have any shape, although they are usually round, square, or rectangular.
Discharge through a sharp-edged orifice may be calculated from:
For instance, if the slot was 1/8' wide the flow rate would likely be less than half of the 1/4', and conversely, if the slot was 1/2' wide the flow rate would likely be greater than doubled. So if anyone can help me out or at least point me in the right direction, it would be much appreciated! Common pipesizes and slot configurations are shown, other sizes up to 48', SCH or SDR'S and slot patterns are available upon request. Slot spacing and slot length is nominal, small variances may occur due to ovality of pipe and the effects of temperature. 14 1/2' 11 3/4'.375' 9 1' 5 2' 3.5 3' 2 6'. The air flow rate through a single vent opening is equal to the total air flow rate V. Divided by the number of single openings; c) since all the analysis parameters are considered average values, it has been assumed K= K in=K out. Enter 1.0472 in the in the flow rate box and choose cubic feet per second from its menu. Click the CALCULATE button and you will see this equals 8 inches. AND you get to see the answer in 5 other different units!! 2) Water is flowing through a 10 centimeter diameter pipe, at a rate of 9 liters per second. What is the water velocity? Air Flow Conversion Calculator Air Velocity is measurement of the rate of displacement of air or gas at a specific location. Air velocity (distance traveled per unit of time) is usually expressed in Linear Feet per Minute (LFM).
Q = Ca?2gh
where
Q= discharge, ft3/s (m3/s)
C =coefficient of discharge
a =area of orifice, ft2 (m2)
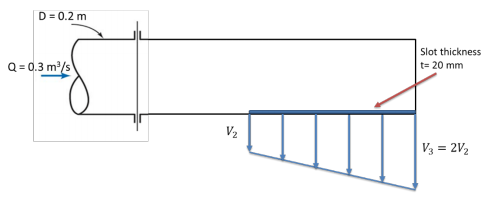
g =acceleration due to gravity, ft/s2 (m/s2)
h =head on horizontal center line of orifice, ft (m)
The coefficient of discharge C is the product of the coef- ficient of velocity Cv and the coefficient of contraction Cc. The coefficient of velocity is the ratio obtained by dividing the actual velocity at the vena contracta (contraction of the jet discharged) by the theoretical velocity. The theoretical velocity may be calculated by writing Bernoulli's equation for points 1 and 2.Thus
V2= ?2gh
The coefficient of contraction Cc is the ratio of the smallest area of the jet, the vena contracta, to the area of the orifice.
Submerged Orifices
Flow through a submerged orifice may be computed by applying Bernoulli's equation to points 1 and 2 in figure below

Values of C for submerged orifices do not differ greatly from those for nonsubmerged orifices.
Weirs can be used to measure flow rates in open channels and rivers - common for water supply and sewage plants
Weirs are structures consisting of an obstruction such as a dam or bulkhead placed across the open channel with a specially shaped opening or notch. The flow rate over a weir is a function of the head on the weir.
Common weir constructions are the rectangular weir, the triangular or v-notch weir, and the broad-crested weir. Weirs are called sharp-crested if their crests are constructed of thin metal plates, and broad-crested if they are made of wide timber or concrete. If the notch plate is mounted on the supporting bulkhead such that the water does not contact or cling to the downstream weir plate or supporting bulkhead, but springs clear, the weir is a sharp-crested or thin-plate weir.
Water level-discharge relationships can be applied and meet accuracy requirements for sharp-crested weirs if the installation is designed and installed consistent with established ASTM and ISO standards.
Rectangular weirs and triangular or v-notch weirs are often used in water supply, wastewater and sewage systems. They consist of a sharp edged plate with a rectangular, triangular or v-notch profile for the water flow.
Broad-crested weirs can be observed in dam spillways where the broad edge is beneath the water surface across the entire stream. Flow measurement installations with broad-crested weirs will meet accuracy requirements only if they are calibrated.
Other available weirs are the trapezoidal (Cipolletti) weir, the Sutro (proportional) weir and the compound weirs (combination of the previously mentioned weir shapes). By combining V-notch weirs with broad chested weirs - larger range of flow can be measured with accuracy.
Rectangular Weir
The flow rate measurement in a rectangular weir is based on the Bernoulli Equation principles and can be expressed as:
q = 2/3 cd b (2 g)1/2 h3/2 (1)
where
q = flow rate (m3/s)
h = elevation head on the weir (m)
b = width of the weir (m)
g = 9.81 (m/s2) - gravity
cd = discharge constant for the weir - must be determined
cd must be determined by analysis and calibration tests. For standard weirs - cd - is well defined or constant for measuring within specified head ranges.

The lowest elevation (h = 0) of the overflow opening of the sharp-crested weirs or the control channel of broad-crested weirs is the head measurement zero reference elevation.
Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Measurement Calculator

cd - discharge constant
b - width of weir (m)
h - height of weir (m)
The Francis Formula - Imperial Units
Flow through a rectangular weir can be expressed in imperial units with the Francis formula
q = 3.33 (b - 0.2 h) h3/2 (1b)
where
q = flow rate (ft3/s)
h = head on the weir (ft) Hollywood casino job openings.
b = width of the weir (ft)
Alternative with height in inches and flow in gpm:
Triangular or V-Notch Weir
The triangular or V-notch, thin-plate weir is an accurate flow measuring device particularly suited for small flows.
For a triangular or v-notch weir the flow rate can be expressed as:
q = 8/15 cd (2 g)1/2 tan(θ/2) h5/2 (2)
where
g =acceleration due to gravity, ft/s2 (m/s2)
h =head on horizontal center line of orifice, ft (m)
The coefficient of discharge C is the product of the coef- ficient of velocity Cv and the coefficient of contraction Cc. The coefficient of velocity is the ratio obtained by dividing the actual velocity at the vena contracta (contraction of the jet discharged) by the theoretical velocity. The theoretical velocity may be calculated by writing Bernoulli's equation for points 1 and 2.Thus
V2= ?2gh
The coefficient of contraction Cc is the ratio of the smallest area of the jet, the vena contracta, to the area of the orifice.
Submerged Orifices
Flow through a submerged orifice may be computed by applying Bernoulli's equation to points 1 and 2 in figure below
Values of C for submerged orifices do not differ greatly from those for nonsubmerged orifices.
Weirs can be used to measure flow rates in open channels and rivers - common for water supply and sewage plants
Weirs are structures consisting of an obstruction such as a dam or bulkhead placed across the open channel with a specially shaped opening or notch. The flow rate over a weir is a function of the head on the weir.
Common weir constructions are the rectangular weir, the triangular or v-notch weir, and the broad-crested weir. Weirs are called sharp-crested if their crests are constructed of thin metal plates, and broad-crested if they are made of wide timber or concrete. If the notch plate is mounted on the supporting bulkhead such that the water does not contact or cling to the downstream weir plate or supporting bulkhead, but springs clear, the weir is a sharp-crested or thin-plate weir.
Water level-discharge relationships can be applied and meet accuracy requirements for sharp-crested weirs if the installation is designed and installed consistent with established ASTM and ISO standards.
Rectangular weirs and triangular or v-notch weirs are often used in water supply, wastewater and sewage systems. They consist of a sharp edged plate with a rectangular, triangular or v-notch profile for the water flow.
Broad-crested weirs can be observed in dam spillways where the broad edge is beneath the water surface across the entire stream. Flow measurement installations with broad-crested weirs will meet accuracy requirements only if they are calibrated.
Other available weirs are the trapezoidal (Cipolletti) weir, the Sutro (proportional) weir and the compound weirs (combination of the previously mentioned weir shapes). By combining V-notch weirs with broad chested weirs - larger range of flow can be measured with accuracy.
Rectangular Weir
The flow rate measurement in a rectangular weir is based on the Bernoulli Equation principles and can be expressed as:
q = 2/3 cd b (2 g)1/2 h3/2 (1)
where
q = flow rate (m3/s)
h = elevation head on the weir (m)
b = width of the weir (m)
g = 9.81 (m/s2) - gravity
cd = discharge constant for the weir - must be determined
cd must be determined by analysis and calibration tests. For standard weirs - cd - is well defined or constant for measuring within specified head ranges.
The lowest elevation (h = 0) of the overflow opening of the sharp-crested weirs or the control channel of broad-crested weirs is the head measurement zero reference elevation.
Rectangular Weir Flow Rate Measurement Calculator
cd - discharge constant
b - width of weir (m)
h - height of weir (m)
The Francis Formula - Imperial Units
Flow through a rectangular weir can be expressed in imperial units with the Francis formula
q = 3.33 (b - 0.2 h) h3/2 (1b)
where
q = flow rate (ft3/s)
h = head on the weir (ft) Hollywood casino job openings.
b = width of the weir (ft)
Alternative with height in inches and flow in gpm:
Triangular or V-Notch Weir
The triangular or V-notch, thin-plate weir is an accurate flow measuring device particularly suited for small flows.
For a triangular or v-notch weir the flow rate can be expressed as:
q = 8/15 cd (2 g)1/2 tan(θ/2) h5/2 (2)
where
θ = v-notch angle
Broad-Crested Weir
For the broad-crested weir the flow rate can be expressed as:
q = cd h2 b ( 2 g (h1 - h2) )1/2 (3)
Measuring the Levels
For measuring the flow rate it's obviously necessary to measure the flow levels, then use the equations above for calculating. It's common to measure the levels with:
Download this game from Microsoft Store for Windows 10, Windows 8.1. See screenshots, read the latest customer reviews, and compare ratings for Texas hold'em Poker Plus. Holdem Manager 3 or Poker Tracker 4 Tracking poker software is necessary for everyone who is playing seriously. Right now poker is all about having information on your opponents and these programs do the job in the best possible way. Texas holdem poker software downloads.
- ultrasonic level transmitters, or
- pressure transmitters
Ultrasonic level transmitters are positioned above the flow without any direct contact with the flow. Ultrasonic level transmitters can be used for all measurements. Some of the transmitters can even calculate a linear flow signal - like a digital pulse signal or an analog 4 - 20 mA signal - before transmitting it to the control system.
Pressure transmitters can be used for the sharp-crested weirs and for the first measure point in broad-crested weir. The pressure transmitter outputs a linear level signal - typical 4-20 mA - and the flow must be calculated in the transmitter or the control system.
Related Topics
- Flow Measurement - Flow metering principles - Orifice, Venturi, Flow Nozzles, Pitot Tubes, Target, Variable Area, Positive Displacement, Turbine, Vortex, Electromagnetic, Ultrasonic Doppler, Ultrasonic Time-of-travel, Mass Coriolis, Mass Thermal, Weir V-notch, Flume Parshall and Sluice Gate flow meters and more
Related Documents
Flow Rate Through Soil
- California Pipe Flow Metering Method - Measure discharge from the open end of partially filled horizontal pipes
- Comparing Flowmeters - A limited comparison of flowmeter principles - regarding service, rangeability, pressure loss, typical accuracy, upstream pipe diameters, viscosity and relative costs
- Flow Rate Calculated based on the Velocity-Area Principle - Flow rate or discharge in an open conduit, channel or river can be calculated with the velocity-area principle
- Flowmeters and Turndown Ratio - Rangeability - Turndown ratio for flow measurement devices like orifices, venturi meters etc.
- Froude Number - Introduction to the Froude Number
- Types of Fluid Flow Meters - An introduction to different types of fluid flowmeters - Orifices, Venturies, Nozzles, Rotameters, Pitot Tubes, Calorimetrics, Turbine, Vortex, Electromagnetic, Doppler, Ultrasonic, Thermal, Coriolis
- Waste Water - Flow Capacity - In sewage piping and pumping systems the fluid flow rate must be kept within certain limits to avoid operating problems
- Weirs - Flow Measurement Standards - Standards of weir flow measurements
Flow Rate Through Tube
Tag Search
Flow Rate Through Slot Machine
- en: weirs notch v-notch flow measurement
- es: medición de flujo v-notch muesca vertederos
- de: Wehren Kerbe V-Kerbe-Durchflussmessung
